
freepik.com
What Is The Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the most common type of cancer found in men. It is the second leading cause of cancer death among men. Prostate cancer is highly treatable in the early stage. Prostate cancer occurs in the prostate gland between the men’s penis and the bladder. It makes some of the fluids that are part of semen. Prostate cancer starts in the cells of the prostate when these cells grow out of control.
What Is The Prostate
medicinenet.com
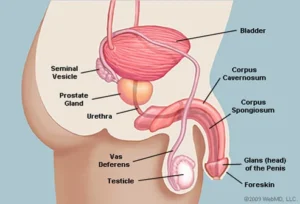
The prostate is a part of the male reproductive system. It includes the penis, prostate, seminal vesicles and testicles. It is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It is the size of a walnut and surrounds the urethra (the tube that removes the urine from the bladder). As a man grows it increases in size and it can cause the urethra to narrow and decrease urine flow.
Growth in the prostate can be of two types:
1. Benign: It is also known as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH):
- It is rare to the threat.
- Don’t attack the nearby tissues.
- It doesn’t spread to other parts of the body.
- It can be removed and can grow back ( but usually doesn’t grow back)
2. Malignant Growth (Prostate Cancer):
- It may be a threat to life.
- It can invade nearby tissue and spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body like lymph nodes or bone.
- It can be often removed and it may grow.
Prostate cancer can spread by travelling through blood vessels or lymph nodes to reach other parts of the body. After spreading cancer cells may attach to other tissue and grow to form new tumours and it causes damage where they land. If prostate cancer transmits to bones, the cancer cells in the bones are also prostate cancer cells. The disease is known as metastatic prostate cancer.
What Are The Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
In the early stage of prostate cancer, there are no symptoms. When symptoms do occur they can be like enlarged prostate or BPH. Prostate cancer can also cause symptoms which are not related to BPH. If a person is suffering from urinary problems consult with a doctor.
Symptoms of prostate cancer include:
- Dull pain in the lower pelvic area.
- Decreased force in the stream of urine.
- Trouble urinating
- Blood in the urine.
- Frequent urinating
- Painful ejaculation
- Bone pain
- Loss of appetite
- Loss of weight
- Bone pain
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Pain in the back, hip or pelvis
What Are The Types Of Prostate Cancer
The types of prostate cancer tell us the type of cell cancer that started. There are different types of prostate cancer. Usually, all prostate cancer is adenocarcinoma. There are two types of adenocarcinoma of the prostate:
There are two types of adenocarcinoma of the prostate:
- Acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate: Most people have this type of prostate. It develops in the gland cells which line the prostate gland.
2. Ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate: It starts in the cell that lines the ducts or tube of the prostate gland. Comparatively, it grows and spreads more quickly than acinar adenocarcinoma.
Other types of cancer that can start in the prostate include:
- Small cell carcinoma
- Sarcomas
- Transitional cell carcinoma
- Neuroendocrine tumours
What Are The Causes Of Prostate Cancer
The causes of prostate cancer are not known yet. Prostate cancer initiates when cells in the prostate develop changes in their DNA. The DNA contains in the cells instructs them what have to do. These changes tell the cells to grow and divide more rapidly than normal cells do. Abnormal cells continue to live even when other cells die.
Abnormal cells accumulate to form tumours, which can grow and invade nearby tissue. Over time, abnormal cells may break down and spread to other parts of the body.
Risk Factors
There are some factors which can increase the risk of prostate cancer:
Older Age:
Prostate cancer is rarely found in men under the age of 40. As men get older the chances of prostate cancer increase. Over the age of 55 chances of damage to the DNA of a prostate cell is more. Damage cell of the prostate begins to grow out of control and forms a tumour.
Family History:
With a family history of prostate cancer risk of prostate cancer in men goes up.
Smoking:
According to research prostate cancer occurs more in smokers.
Diet:
Poor diet increases the risk of prostate cancer. If a person eats more calories, animal fats, and refined sugar, and does not enough foods and vegetables. Obesity is known to increase a man’s risk of dying from prostate cancer.
Disclaimer: All the content of this article is for information purposes only.
References:

 Myocardial Infarction- Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Myocardial Infarction- Symptoms, Causes & Treatment Malaria: Causes, Symptoms & Diagnosis
Malaria: Causes, Symptoms & Diagnosis Heart Attack: Symptoms & Risk Factors
Heart Attack: Symptoms & Risk Factors Cervical Cancer: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Cervical Cancer: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment


