
https://www.caffeineinformer.com/top-10-soft-drinks
“Stay Healthy, Avoid the Risk Effects of Carbonated Drinks!”
Introduction
Carbonated drinks are a popular beverage choice for many people, but they can have some serious health risks associated with them. Carbonated drinks contain carbon dioxide, which can cause bloating, gas, and other digestive issues. They also contain high amounts of sugar, which can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of diabetes and heart disease. Additionally, the acidity of carbonated drinks can damage tooth enamel and lead to cavities. This article will discuss the potential risks associated with drinking carbonated beverages.
Carbon dioxide includes in carbonated drinks and the presence of this gas generated bubbles and fizzes in the liquid. Carbonation is the addition of carbon dioxide to a beverage. It imparts a sparkle and tangy taste and prevents spoilage.
The Health Risks of Consuming Too Much Carbonated Drink
The consumption of carbonated drinks has become increasingly popular in recent years, with many people drinking them on a daily basis. While these drinks can be refreshing and enjoyable, it is important to be aware of the potential health risks associated with consuming too much of them.
Carbonated drinks contain a variety of ingredients, including sugar, caffeine, and artificial sweeteners. The high sugar content of these drinks can lead to an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and dental cavities. Caffeine can also have a negative effect on health, as it can cause insomnia, anxiety, and headaches. Artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame, have been linked to an increased risk of cancer and other health problems.
In addition to the health risks associated with the ingredients in carbonated drinks, the carbon dioxide gas used to carbonate them can also have a negative effect on health. The gas can cause bloating, gas, and stomach discomfort. It can also increase the risk of acid reflux and heartburn.
Risk Effect Of Carbonated Drink
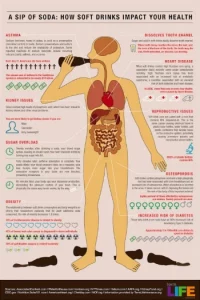
https://www.krautsource.com/blogs/news/9-health-hazards-of-soft-drinks
Risk of Diabetes and Heart Disease
Carbonated drinks, such as sodas, energy drinks, and sparkling water, have become increasingly popular in recent years. While these beverages may be refreshing and enjoyable, research has suggested that they may be associated with an increased risk of diabetes and heart disease.
Studies have found that consuming carbonated drinks is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. This is likely due to the high sugar content of many carbonated drinks, which can lead to elevated blood sugar levels. Additionally, the carbonation process can cause the body to absorb sugar more quickly, leading to a rapid rise in blood sugar levels.
In addition to diabetes, research has also suggested that consuming carbonated drinks may increase the risk of heart disease. This is likely due to the high levels of caffeine found in many carbonated drinks, which can lead to elevated blood pressure and an increased risk of stroke. The Carbonation process can cause the body to absorb caffeine more quickly, leading to a rapid rise in blood pressure.
Risk Of Digestive Health
Carbonated drinks can have a negative impact on digestive health. This article will discuss the effects of carbonated drinks on digestive health.
The carbon dioxide gas in carbonated drinks can cause bloating and gas in the stomach. This is because the gas is released in the stomach and can cause the stomach to expand, leading to discomfort. Additionally, the gas can cause belching and flatulence.
The sugar content of carbonated drinks can also have a negative effect on digestive health. The sugar can cause an increase in the number of bacteria in the gut, leading to an imbalance in the gut microbiome. This can lead to digestive issues such as bloating, constipation, and diarrhoea.
The acidity that occurs due to carbonated drinks can cause irritation to the lining of the stomach and intestines, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Additionally, acidity can interfere with the absorption of nutrients, leading to deficiencies.
Finally, the caffeine content of carbonated drinks can have a negative effect on digestive health. The caffeine found in carbonated drinks may increase stomach acid production, leading to heartburn and indigestion. Additionally, caffeine can cause an increase in the production of bile, leading to diarrhoea.
The Link Between Carbonated Drinks and Weight Gain
Recent studies have suggested a link between carbonated drinks and weight gain. Carbonated drinks, such as sodas, energy drinks, and sparkling waters, contain high levels of sugar and calories, which can contribute to weight gain.
The sugar in carbonated drinks is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, causing a rapid rise in blood sugar levels. This can lead to an increase in hunger and cravings for more sugary foods. Additionally, the calories in carbonated drinks are not filling, meaning that they do not provide the same feeling of fullness as other foods. This can lead to overeating and weight gain.
Furthermore, carbonated drinks can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate its energy balance. Studies have shown that drinking carbonated beverages can lead to an increase in the body’s fat storage, as well as an increase in the body’s fat-storing hormones. This can lead to an increase in overall body fat, which can contribute to weight gain.
Finally, carbonated drinks can also lead to dehydration. Dehydration can cause fatigue, which can lead to a decrease in physical activity and an increase in sedentary behaviour. This can further contribute to weight gain.
In conclusion, there is a clear link between carbonated drinks and weight gain. Therefore, it is important to limit the consumption of carbonated drinks in order to maintain a healthy weight.
The Impact of Carbonated Drinks on Teeth and Bone Health
Carbonated drinks, such as sodas, energy drinks, and sparkling waters, are popular beverages that are consumed by people of all ages. While these drinks may be enjoyable but the acidity of carbonated drinks can erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities and other dental problems. The sugar content of these drinks can also contribute to tooth decay. Additionally, the carbonation in these drinks can cause the enamel to soften, making it more susceptible to damage.
The phosphoric acid found in many carbonated drinks can also have a negative effect on bone health. Phosphoric acid can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb calcium, which is essential for strong bones. This can lead to an increased risk of osteoporosis and other bone-related conditions.
In order to protect teeth and bones, it is important to limit the consumption of carbonated drinks. If these drinks are consumed, it is best to drink them with a straw and rinse the mouth with water afterwards. Hence it is important to drink plenty of water throughout the day to help keep teeth and bones healthy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the risk effects of carbonated drinks are numerous and should not be taken lightly. While they may provide a refreshing and enjoyable beverage, they can also lead to serious health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and tooth decay. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with consuming carbonated drinks and to limit their consumption.
References:

 Hobbies: The Power Of In Refreshing Mood
Hobbies: The Power Of In Refreshing Mood Millets : Adapt Millet In Your Life Style
Millets : Adapt Millet In Your Life Style Diabetes Supplements: A Comprehensive Guide
Diabetes Supplements: A Comprehensive Guide


