
livescience.com
Introduction
Nucleic Acids are the organic material present in the living organism. These nucleic acids are present in the form of DNA or RNA. Nucleic Acids are the combination of nitrogenous bases, sugar molecules and phosphate groups that are linked by different bonds.
What Is DNA?
DNA or Deoxyribonucleic acid is the hereditary material of the organism. DNA molecule is a group of molecules that carries genetic information and transfers it from parents to their offspring. DNA is found in the nucleus, but a small amount of DNA is also present in the mitochondria (the structure that presents within the cells converts of eukaryotic.
visiblebody.com
Structure Of DNA
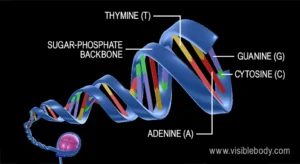
James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the DNA in 1935. DNA molecule consists of two strands and forms helix structures. Each strand of DNA molecule has a backbone of ribose sugar (deoxyribose sugar) and phosphate groups. Each sugar is attached to one of four nitrogenous bases- Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine.

youtube.com
- These nitrogenous bases are categorized into purines and pyrimidines-
Purine- Adenine & Thymine, Pyrimidine- Guanine & Cytosine
- In DNA molecule Adenine attaches with Thymine with two hydrogen bonds and Guanine is attached with cytosine with three hydrogen bonds.

ib.bioninja.com.au
- Each nitrogenous base is attached to a sugar molecule and phosphate groups make nucleotides.
Nitrogenous bases+Sugar Molecules+Phosphate Groups=Nucleotide
- These nucleotides are arranged in two long strands coiling around each other to form a double helix structure.
- These two DNA strands are called polynucleotides because they are made up of monomer units i.e. nucleotides.
- Each DNA strand has a 5′ end with a phosphate group and a 3′ end with a hydroxyl group.
- These strands of DNA molecule are antiparallel as one strand moves in a 5′ to 3′ direction and the other strand moves in a 3′ to 5′ direction.
- DNA is composed of deoxyribonucleotide and deoxyribonucleotides are linked together by 3′-5′ phosphodiester bonds.
- The diameter of the double helix is 2 nm and the pitch between two consecutive base pairs is 0.34 nm.
- The double helix structure repeats at an interval of 3.4 nm corresponding to 10 base pairs.
- DNA molecule has two asymmetric grooves: Major Grooves & Minor Grooves.

khanacademy.org
- Due to the geometrical configuration of the bonds between the phosphate, sugar and base groups to attach at 120-degree angles.
Types Of DNA:
A-DNA: It was first identified by X-ray diffraction at 75 % humidity. A type of DNA is a right-handed helix and gives major and minor grooves. It is similar to B-type DNA.

in.pinterest.com
B-DNA:
It is the most common form of DNA. It is commonly known as the Watson and Crick model of DNA. It is a right-handed double helix structure. It was identified at 92% relative humidity.
Z-DNA:
Z- DNA is a left-handed double helix structure. It is a complementary nucleotide with alternating purines and pyrimidines and forms Z form at high salt concentrations. The Z DNA was discovered by Andres Wang and Alexander Rich. This DNA is a double helix in a zigzag form.
Conclusion: DNA is the basic and essential structure of human life. The discovery of DNA is a major development in the field of research. The discovery of DNA defines the importance of DNA in our lives and the existence of DNA makes sense that DNA has affected our lives in so many areas.
Disclaimer: All the content of this article is for information purposes only.
References: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26821/

 Ribonucleic Acid (RNA): Structure, Types & Properties
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA): Structure, Types & Properties Gel Electrophoresis: Types and Properties
Gel Electrophoresis: Types and Properties PCR: Polymerase Chain Reaction
PCR: Polymerase Chain Reaction



[…] virus has an enveloped shaped double-stranded DNA. It belongs to the family Poxviridae and the genus Orthopoxvirus which includes camelpox, cowpox, […]
[…] known yet. Prostate cancer initiates when cells in the prostate develop changes in their DNA. The DNA contains in the cells instructs them what have to do. These changes tell the cells to grow and […]
[…] of instructions given by DNA into a functional protein. Molecular biology states that “DNA makes RNA and RNA make […]
[…] virus is an infectious unicellular organism consisting of DNA or RNA nucleic acid. The genetic material of the virus DNA or RNA coated with protein. A virus […]
[…] an essential role in the formation of blood, cell metabolism, nerve function and the production of DNA. However, our bodies do not make vitamin B12 but we can get it from animal-based foods or from […]
[…] DNA absent […]